
Joint pain can make life unbearable.After the doctor's visit, an overview of diagnosed arthrosis or arthritis will appear from the outpatient clinic.
People who are far from medicine have little idea of the difference between arthritis and osteoarthritis, and mistakenly consider them to be the same disease.
In fact, these are two completely different pathological processes that can occur simultaneously.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis refers to degenerative-inflammatory processes and develops due to age-related changes in the structure of cartilage tissue.
It affects the moving joints of large bones, and less commonly, the joints of the fingers.
Appearance of a joint with osteoarthritis
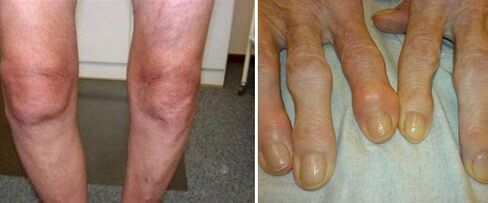
The main cause of pathological changes is metabolic disturbances in the cartilage.Violation of cartilage trophism leads to irreversible loss of proteoglycans and loss of tissue elasticity.
Dystrophic changes in cartilage cause pathological changes in the structure of the articular surfaces of bones.Over time, the degeneration process spreads to the periarticular tissues.
Types of osteoarthritis
Based on their origin, they distinguish between primary and secondary osteoarthritis.
The primary form affects previously healthy joints and is a consequence of age-related changes and insufficient physical activity.The timing of the appearance of the first symptoms of osteoarthritis depends on hereditary predisposition, characteristics of professional activity and lifestyle.
Traditionally, people over 45 are considered in the risk group, but now there is a steady trend towards early occurrence.The disease mainly affects women, but with age the dependence on gender gradually levels off.
Secondary arthrosis develops on the basis of a previous injury or certain diseases of a different nature, including:
- autoimmune processes;
- metabolic disorders;
- endocrine dysfunction;
- pathologies of the structure of bone joints;
- genetic diseases;
- inflammatory processes.
Secondary osteoarthritis is not associated with the aging process and can occur at any age.
There are three stages in the development of the disease.
In the first stage, changes occur in the synovial fluid.The nutrition of the cartilage is disrupted and its resistance to stress decreases.Roughness appears on the surface of the cartilage, and inflammation develops, accompanied by pain.
As the disease progresses to the second stage, the pain becomes habitual and the course of the accompanying inflammation becomes wave-like.The cartilage begins to deteriorate and compensatory bone growth forms at the edges of the articular area.Periarticular muscles are involved in pathological processes.
The third stage is characterized by severe depletion of articular cartilage with areas of complete tissue destruction.Degenerative processes lead to irreversible anatomical changes, including changes in the axis of the limb.The function of the ligament apparatus is disturbed, abnormal mobility appears in the affected joint against the background of limited natural mobility.
According to the location of the lesion, they are distinguished:
- gonarthrosis,
- coxarthrosis,
- spondyloarthrosis,
- arthrosis in the interphalangeal joints of the hands.
Other localizations of pathology are relatively rare.
Gonarthrosis, arthrosis of the knee joint
Risk factors for the development of this disease include hereditary predisposition, overuse or knee injuries due to occupational characteristics.
According to statistics, arthrosis lesions in the knee joints are diagnosed more often in women.
In the early stages of development, the disease manifests itself as discomfort in the affected joint and aching pain.Depending on the causes of the lesion, several forms of gonarthrosis are distinguished.
Some of them are characterized by a prolonged lack of progression;the patient's condition remains stable for decades.But there are also those that develop quickly and lead to loss of mobility of the affected limb.
Coxathrosis, arthrosis of the hip joint

With this disease, a classic clinical picture of osteoarthritis is observed.
The first symptom of coxarthrosis is discomfort in the hip joint after physical activity.
In progressive coxarthrosis, the pain increases, stiffness and limited mobility occur.
Patients with a severe form of coxarthrosis spare the affected limb, avoid stepping on it and, while stationary, choose positions where the pain is felt the least.
Spinal arthrosis, spondyloarthrosis
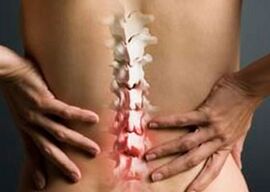
Spondyloarthrosis refers to pathologies that develop against the background of degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs.
The first and most important symptom of developing spinal osteoarthritis is pain when bending from side to side or back and forth.
When a person takes a horizontal position, the pain gradually subsides.
Over time, in the absence of adequate treatment, the mobility of the affected part of the spine can be completely lost.
Without appropriate treatment, spinal osteoarthritis can cause intervertebral hernias and joint deformation.In severe cases, the patient loses the ability to perform usual movements and becomes disabled.
Osteoarthritis of the interphalangeal joints of the hands
The disease primarily affects women.Among the early symptoms of osteoarthritis are pain on contact with cold water and on straining the fingers.Over time, the joints become deformed due to the compression of adjacent tissues and the formation of characteristic bone growths.
The disease has a wave-like course, in the acute stage the joints swell, partially lose mobility, and the tactile sensitivity may be reduced.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
It is impossible to cure osteoarthritis completely with modern medicine.But timely diagnosis and complex therapy aimed at preventing further destruction of cartilage tissue help to stabilize the condition of the affected joint and significantly improve the patient's quality of life.
First of all, it is necessary to reduce the load on the musculoskeletal system.Doctors recommend avoiding carrying heavy objects, staying in one position for a long time and limiting time on your feet.For obese patients, losing weight is essential.
The following are used for drug treatment of osteoarthritis:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, internally in the form of injections or tablets and externally as part of ointments.The form and regimen of use are prescribed depending on the patient's condition;
- drugs from the group of chondroprotectors to maintain the condition of cartilage tissue;
- steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of intra-articular injections.Prescribed in severe cases;
- hyaluronic acid preparations to improve joint mobility.
In addition, heat compresses and ointments, drugs that activate blood microcirculation and metabolic processes, antioxidants and microelement-vitamin complexes with selenium are used, and physiotherapeutic treatment is prescribed.In severe cases, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention.
During the remission period, the patient is recommended a course of exercise therapy, selected in accordance with the characteristics of the course of the disease.
Gout
Gout is an inflammatory disease that occurs as an underlying disease, a concurrent pathology or as a complication of a previous infectious disease.
Appearance of joints with arthritis
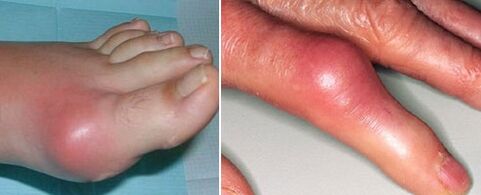
Among the typical causes of inflammatory processes in the joints:
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- lack of vitamins;
- damages;
- autoimmune diseases;
- infectious lesions of various etiologies.
In contrast to osteoarthritis, pathological processes in arthritis affect the periarticular tissues.The appearance of pain does not depend on physical activity and body position, and often bothers you at night.
Noise in the joints, characteristic of the early stages of osteoarthritis, is rarely observed.A general blood test indicates the presence of an inflammatory process;when examining joints, characteristic degenerative changes in cartilage are rarely detected.
The common symptom of both diseases is pain.Any unusual and unpleasant sensations in the joints are a good reason to consult a doctor.The success of the treatment largely depends on timely detection and treatment of the disease.
Types of arthritis
Based on their occurrence, gout is divided into several types:
- infectious arthritis.They develop as independent diseases due to infection of wounds (primary infectious arthritis) or when a pathogen enters the bloodstream from organs affected by infection (secondary arthritis);
- rheumatoid arthritis.This chronic disease is of infectious autoimmune origin and usually develops in middle-aged and elderly people;
- uric acid gout.The inflammatory process is caused by microtraumatization of the cartilage surface by crystals of uric acid salts formed in the joint capsule;
- traumatic arthritisdevelops as a response to trauma, but may develop several years after the consequences have been eliminated;
- juvenile rheumatoid arthritisaffects children under the age of 16.The causes of this disease are not yet known.The course is chronic, progressive.
The course of arthritis can be acute or chronic.In the acute course, the disease develops rapidly, with severe swelling, severe pain in the affected area, local or general temperature rise.
In chronic arthritis, the symptoms increase gradually, and the disease can develop over years.With untimely or inappropriate treatment, acute arthritis can become chronic.
According to the characteristics of the lesion, monoarthritis and polyarthritis are distinguished.In monoarthritis, the lesion is localized on one of the joints;when several joints are involved in the pathological process, a diagnosis of polyarthritis is made.
Gout treatment
The treatment strategy for gout depends on the causes of the disease and the severity of the patient's condition.For infectious arthritis, patients are prescribed a course of antibiotics or other drugs in accordance with the nature of the pathogen.
To eliminate inflammation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used in the form of injections, tablets and/or externally in the form of an ointment or gel.
In addition, drugs from the groups of chondroprotectors, antihistamines and general restorative agents can be prescribed.In some cases, patients are prescribed medication that improves blood microcirculation.
In addition to drug therapy, patients are prescribed a course of physiotherapeutic procedures and, during the remission period, a set of exercise therapy exercises.
In severe and advanced cases, surgery may be necessary.
Without the help of specialists, arthritis and osteoarthritis can lead to disability.
Self-medication for joint diseases is contraindicated;in the vast majority of cases, the patient's condition gradually worsens.
Any change in the functionality of the joint is a reason to visit a doctor.
Preventive measures
In order to prevent arthritis and arthrosis, it is important to optimize physical activity so as to avoid overload.People diagnosed with the disease, as well as those at risk, must adjust their diet in favor of healthy foods, reduce alcohol consumption and stop smoking.
People who are prone to obesity are advised to maintain normal body weight, as increased load on the musculoskeletal system can induce or accelerate pathological changes.
For timely detection of the disease in the early stages, it is important to undergo regular preventive examinations.




























